Pasteurized vs. Raw Milk & Dairy
 The milk and dairy today on the supermarket shelves is far from the healthy, traditional dairy products eaten over centuries past. Today, it is homogenized, pasteurized, comes from factory-farmed cows fed unnatural diets of GMOs, and if it is not organic, typically contains antibiotic and pesticide residue.
The milk and dairy today on the supermarket shelves is far from the healthy, traditional dairy products eaten over centuries past. Today, it is homogenized, pasteurized, comes from factory-farmed cows fed unnatural diets of GMOs, and if it is not organic, typically contains antibiotic and pesticide residue.
In an attempt to force cows into increased milk production, the milk industry also began the widespread use of genetically engineered "bovine growth hormone," also known as BST. Both the European Union and Canada have banned the use of BST due to associated health risks.
- Understanding GMOs & the health risk
- What is factory farming & why is it banned in other countries
- Why factory-farmed meat is dangerous for your health
Raw dairy was a staple product many traditional cultures worldwide that suffered none of the health issues we experience today. These cultures were robust and strong, and lived well into old age without the bone-related conditions synonymous with old age in our industrialized western world. As you will see, there is a direct correlation between pasteurized dairy and bone-related diseases such as osteoporosis.
Learn about the diets of traditional cultures...
What Exactly Is Pasteurization?
Pasteurized milk products have been heated at high temperatures for a specific length of time to kill most microorganisms living within it. Pasteurization is named after the 19th-century French scientist Louis Pasteur, who published "The Germ Theory of Disease."
The two most common types of pasteurization in the US are:
- Traditional Pasteurization: Milk is heated to a minimum of 161° for 15 seconds
- Ultra Pasteurization: Milk is heated to 280° for 2 seconds
Why Pasteurize?
The biggest claim for requiring milk to be pasteurized is to kill bacteria. But like irradiated foods, pasteurized foods give us a false sense of security. If food is contaminated, irradiation and pasteurization can kill the contamination. Many meat and dairy products are contaminated as a result of unsanitary and highly questionable factory-farming practices. Animals are abused and kept in filthy conditions, and the only way they can remain disease-free is to pump them with a continual stream of antibiotics (up to 80% of antibiotics in the US is used by the agricultural industry).
Irini |
Instead of addressing sanitation issues and abolishing the use of medicated additives, irradiation and pasteurization covers up the problem and serves as a convenient excuse to not shape up and clean up the food production environment. Milk producers can now be less careful about high standards of cleanliness - why bother if you are going to pasteurize or irradiate it? Over the past 20 years, Organic Pastures in California has produced millions of gallons of raw milk and experienced not one reported illness, whereas pasteurized milk products have generated at least 19 product recalls.
Breast milk itself is definitely not sterile and free of bacteria - far from it. Breast milk is very high in pathogens. But the bioactive components in "raw" breast milk assist the baby in developing a strong immunity for life to protect against any pathogens they comes in contact with. Should we expect health experts to begin demanding that breast milk be pasteurized?
The only time cow's milk should ever be drank is if it comes from pasture-raised (free-range) cows at an organic facility that has high standards of cleanliness. This means that the cows are eating their natural food source (rather than highly processed GMO products), and it also means that there are no antibiotics or other chemicals present in the milk.
Unpasteurized (raw) milk is always best. Read on to find out why.
What Pasteurization Does to Milk
Calcified Tissue Int'l(4) |
Pasteurization heats the milk to a temperature that causes the milk to undergo significant changes. Beneficial bacteria, nutrients, and enzymes are destroyed, including ingredients that are natural protectors of the milk and help our bodies predigest the milk proteins. This is why some people are unable to properly digest pasteurized milk, and yet have no problem digesting raw milk.
"Enriched" or "Fortified"
Manufacturers then attempt to enrich the milk by adding back lab-made chemical versions of the nutrients that were originally present but are now destroyed (e.g. synthetic calcium). They may also fortify the milk by adding chemical nutrients that were never in the food to begin with (e.g. synthetic vitamin D).
There is a significant difference between breast milk, raw milk, and pasteurized milk. Let's compare the three and see what these differences are:
| Component | Breast Milk | Raw Milk | Pasteurized Milk | UHT Milk | Infant Formula | |||||
| B-lymphocytes | active | active | inactivated | inactivated | inactivated | |||||
| Macrophages | active | active | inactivated | inactivated | inactivated | |||||
| Neutrophils | active | active | inactivated | inactivated | inactivated | |||||
| Lymphocytes | active | active | inactivated | inactivated | inactivated | |||||
| IgA/IgG Antibodies | active | active | inactivated | inactivated | inactivated | |||||
| B12Binding Protein | active | active | inactivated | inactivated | inactivated | |||||
| Bifidus Factor | active | active | inactivated | inactivated | inactivated | |||||
| Medium-Chain FAs | active | active | reduced | reduced | reduced | |||||
| Fibronectin | active | active | inactivated | inactivated | inactivated | |||||
| Gamma-Interferon | active | active | inactivated | inactivated | inactivated | |||||
| Lactoferrin | active | active | reduced | inactivated | inactivated | |||||
| Lysozyme | active | active | active | inactivated | inactivated | |||||
| Mucin A/Oligosaccharides | active | active | reduced | reduced | inactivated | |||||
| Hormones/Growth Factors | active | active | reduced | reduced | inactivated | |||||
Source: The Lancet, 17 Nov 1984;2(8412):1111-1113
Now let's take a look at the damaging effects of pasteurized products when it comes to our bodies:
- Pasteurization Damages Protein Content
Pasteurization causes the casein (milk protein) to coagulate and toughen, making it less available to the body. This contributes to the development of childhood allergies and eczema due to the protein becoming denatured from the pasteurization process. - Pasteurization Destroys Enzymes
In its natural state, raw milk contains all the appropriate digestive enzymes to help us efficiently digest the milk protein and fat, but these enzymes are destroyed by pasteurization. These enzymes are present in a mom's breast milk.(1) - Pasteurization Destroys Calcium & Other Nutrients
During pasteurization, milk is heated to the point that renders the calcium unusable. The unabsorbed calcium is then deposited in the soft tissues of the body to calcify. This is a primary reason that rates of osteoporosis and bone-related diseases are highest in western countries that drink the most pasteurized dairy products, and a reason children suffer more dental deformities than ever before (see below).
Pasteurization also damages other nutrients such as vitamin C and iodine.
Unfortunately, pasteurization is now only one of many concerns. In today's industrialized food chain, dairy and milk products not only contain pasteurized milk, but they are also filled with all sorts of undesirables such as processed sugars, artificial colors and flavors, and a variety of unpronounceable chemicals. It is hard to justify anything good about them at all, except that the containers look bright and pretty... Milk-based drinks are a primary cause of mucus build-up in children.
Raw Milk vs. Pasteurized Milk - Health Concerns
According to the FDA, health benefits claimed by raw milk advocates "do not exist." This is in spite of very evidence to the contrary that shoes the opposite: Health issues result from drinking pasteurized milk. Government agencies and the dairy industry are heavily biased against raw dairy, while providing incomplete facts or erroneous statistics about the healthful properties of pasteurized milk products.
False Claims Against Unpasteurized Milk
In an FDA PowerPoint presentation warning against raw milk,(9) 15 studies were cited. In all 15 studies:
80% had no valid positive milk sample
67% had no valid statistical association with raw milk
47% had findings misrepresented by the FDA
33% had alternatives that were discovered but not pursued
13% had no evidence anyone consumed a raw milk product
13% had no outbreak that existed
100% did not show that pasteurization would have prevented an outbreak
Unpasteurized dairy is not more dangerous to consume than pasteurized dairy. Every study vilifying milk for outbreaks has been misquoted and unable to prove that pasteurization of that same milk could have prevented the outbreak.
The FDA: Failure to protect on a mass scale...
Consider this comparison of raw vs. pasteurized milk in California, where raw milk is legal:
- Since 1999, 40 million servings of Organic Pastures raw milk have been produced with not one reported illness.
- 19 recalls of pasteurized milk products occurred during that same period.
Could raw milk become contaminated due to unclean practices, or because of how the milk is handled on the way to the consumer? Of course! The same could be said of any food. This is the reason why we have had more recalls of pasteurized milk than raw milk. We only need to look at the serious consequences of trusting government agencies to understand how questionable food handling practices and a lack of quality control can fatally contaminate our food.
Choose Raw Dairy
Raw (unpasteurized) cheese is now available in every major grocery chain across the country, with some natural food stores carrying a significant selection from all around the world. Raw milk is also available in several states throughout the US, including:
Arizona  California
California  Connecticut
Connecticut  Idaho
Idaho  Maine
Maine  New Hampshire
New Hampshire
New Mexico  Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania  South Carolina
South Carolina  Washington
Washington
For an up-to-date state-by-state list, check out Farm to Consumer to determine your state law.
Raw dairy & why you should choose it...
RELATED ARTICLES
- Why kids are getting sicker & fatter
- Before birth - prenatal care
- Baby's first food
- Beginning solid food
- Healthy eating guide for children
- Why breast feeding is important
- Bone broth
- Pasteurized vs. raw dairy
- The health benefits of raw milk
- The importance of organic during pregnancy
- Serious dangers of pesticides in our food
- Vaccinations & children
- Healthy, strong teeth
- Tips on raising happy & healthy children
- Nurturing creativity & individuality
- Discipline & setting boundaries



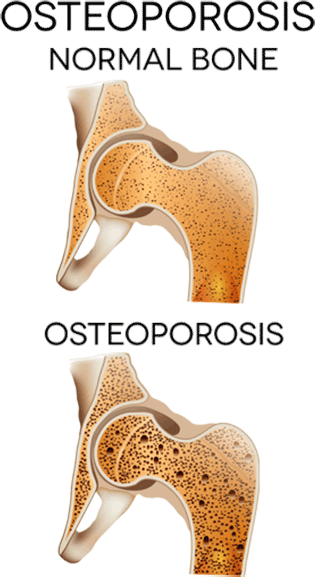 Contrary to what the milk industry will have you believe, pasteurized dairy does not prevent osteoporosis or bones fractures at all. In fact, it does the opposite.
Contrary to what the milk industry will have you believe, pasteurized dairy does not prevent osteoporosis or bones fractures at all. In fact, it does the opposite.